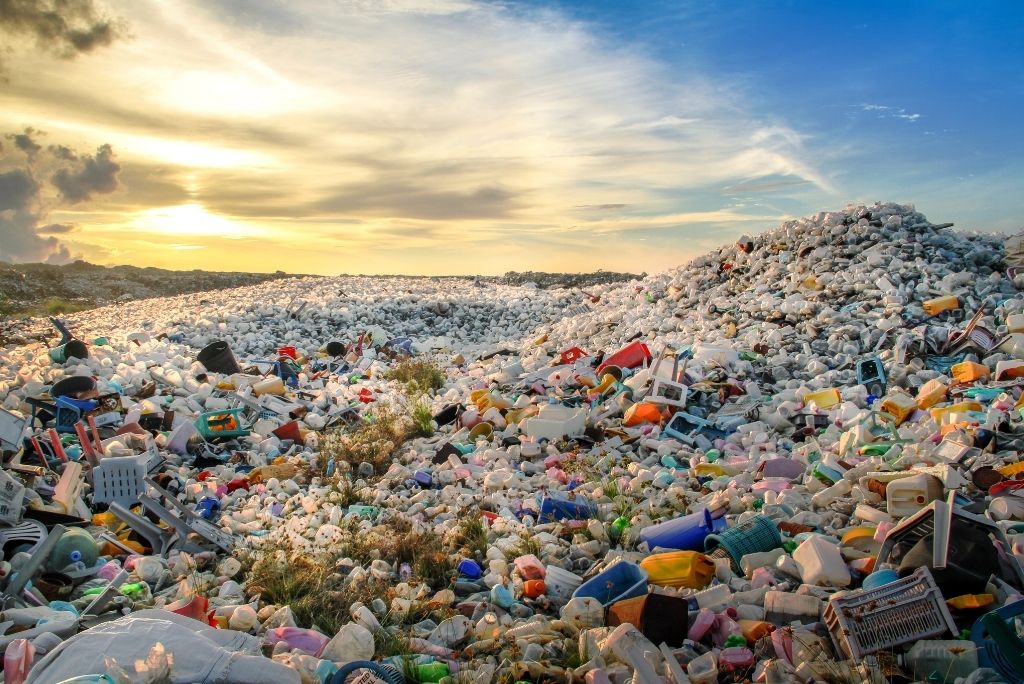
The Environmental and Economic Impact of Poor MSW Management
When waste management systems fail, communities bear the burden—environmentally, economically, and socially.
By recognizing the full impact of poor municipal solid waste (MSW) management, city leaders can make informed decisions that protect public health, reduce costs, and create new value for their communities.
The Environmental Costs of Outdated Waste Systems
Mismanaged waste doesn’t just pile up—it seeps into our air, water, and soil, accelerating climate change and putting ecosystems and public health at risk.
Cities that rely on outdated waste disposal methods only worsen these environmental pressures, making it harder to protect the public and meet sustainability goals. Recognizing these consequences is the first step toward implementing more effective waste solutions.
1. Climate Change and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Costs
Landfills release massive amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas that accelerates climate change. In the U.S., these substances rank as the third-largest source, contributing 14.5% of total emissions in the short term.
Beyond the dump, incineration also releases harmful pollutants, impacting both air quality and climate stability.
Advisor Insight: Methane mitigation is one of the fastest ways to slow climate change. Cities with high organic waste volumes are uniquely positioned to make a measurable impact.

2. Groundwater Contamination and Soil Pollution
Toxic leachate, which is a chemically saturated liquid that drains or ‘leaches’ from landfills, can seep into groundwater, raising concerns for long-term environmental quality and potential impacts on public health.
This contaminated runoff can include harmful substances such as heavy metals, ammonia, and organic compounds. Over time, these contaminants accumulate in the soil, making land unsuitable for agriculture, development, or safe public use.
3. Air Pollution and Public Health Risks
Open dumping and waste burning can release harmful pollutants, such as dioxins and furans, that may affect air quality and contribute to health concerns like respiratory or cardiovascular conditions.
Dioxins are toxic chemical compounds formed during the burning of materials like plastics and industrial waste. They are classified as known human carcinogens and can disrupt hormones, immunity, and reproductive health.

Furans, also created through combustion, share similar toxic properties. They persist in the environment and can accumulate in soil, water, and the food chain, posing long-term risks to both ecosystems and public health.

Communities located near poorly managed waste sites face increased environmental risks over time, while simultaneously experiencing significant economic impacts.
The Economic Burdens of Traditional Waste Disposal
For many municipalities, the costs are outpacing budgets, creating financial constraints that limit investment in better systems. Cities dependent on traditional waste systems face not only direct costs like hauling and tipping fees but also long-term liabilities tied to infrastructure upkeep and environmental mitigation.
1. The True Cost of Landfills
The costs of landfills go far beyond their initial construction. Expenses can range from $80,000 to $500,000 per acre, not including the cost of land acquisition, permitting, and regulatory compliance.
And even after a landfill closes, cities remain responsible for decades of post-closure maintenance, groundwater monitoring, and environmental remediation.
These costs continue to grow as population and waste volumes increase and available land becomes scarce.
2. The Unsustainable Costs of Incineration
Incineration facilities cost between $190 million and $1.2 billion to build and have high operational expenses. Despite these high costs, many regions in the United States still burn their waste.
However, burning waste doesn’t eliminate waste—it only changes its form, leaving behind ash and toxic emissions.
Additionally, cities utilizing incineration methods manage steps like ash disposal, pollution controls, and public resistance, all of which contribute to a costly cycle with diminishing returns.

It does not need to be this way. Your communities deserve better.
How Cities Can Turn Waste Into a Resource
The limitations of outdated waste systems are clear, but so is the path forward. To move from burden to benefit, cities need systems that recover more, cost less, and scale with growing demands. That starts with better waste diversion and technology that turns organic waste into value.
Waste Diversion
Waste diversion is one of the most direct and impactful ways to reduce costs and reclaim value. By keeping recyclables, compostables, and organics out of landfills, cities avoid tipping fees, reduce emissions, and generate new revenue streams.
Scalable Waste Diversion Solutions
Cities need effective and practical solutions that integrate with existing infrastructures while maximizing efficiency. These are not pilot programs or future promises. They’re proven systems that work in real communities today.

Anaerobic digestion turns food waste into clean energy and nutrient-rich fertilizer.
Waste-to-energy systems recover usable output while reducing landfill dependency.
Did You Know: BurCell® Technologies leads in waste diversion. Our system accelerates the separation of organics from municipal solid waste, enabling rapid recovery and higher volumes of valuable material. Cities using BurCell® experience up to 75% diversion success.
Additionally, BurCell’s proprietary process transforms organic waste into RevitaFuel™ SF—a clean, renewable solid fuel that supports industries aiming to meet their sustainability targets.
The Time to Move Forward is Now
The costs of poor waste management are too high to ignore.
Modernizing your waste system starts with leadership. Cities that update procurement policies, expand infrastructure for composting and recovery, engage and educate their communities, and use data to drive decisions are creating more resilient operations.
Explore how the BurCell® System can help your community reduce landfill waste, recover valuable resources, and build a cleaner, more efficient future.

Why Is Municipal Solid Waste One of the Most Challenging Types of Waste to Manage?
Municipal solid waste presents unique management challenges because of its diverse waste streams, complex composition, and the scale required for effective MSW management systems. Unlike industrial or hazardous waste with predictable characteristics, MSW contains everything from food scraps and plastics to electronics and yard debris—each requiring different processing methods, infrastructure, and disposal solutions.
What We Know About the Growing Complexity of MSW Management
Managing municipal solid waste (MSW) is a growing challenge for cities worldwide. With global waste generation projected to reach 3.8 billion tons by 2050, traditional waste management systems are struggling to keep pace.
Cities face growing landfill constraints, rising costs, and increasing environmental pressures—yet waste isn’t just a problem to be solved; it’s an opportunity to be redefined. Your community deserves a smarter, cleaner, and more sustainable approach to waste management.
Conventional “collect-and-dispose” models are no longer enough. Waste streams are evolving, regulatory demands are tightening, and public expectations for sustainable solutions are higher than ever.
What Is Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)?
Municipal Solid Waste consists of everyday materials discarded by households, businesses, and institutions. These materials range from food scraps and plastics to packaging, yard waste, and hazardous items.. Understanding the composition of MSW is key to designing effective waste management strategies.
The complexity of MSW in solid waste management lies in its heterogeneous nature; no two communities generate identical waste profiles, making standardized solutions challenging to implement.
Breaking Down Diverse Waste Streams
Different waste streams within MSW require distinct management solutions, making MSW management more challenging than handling uniform waste types. By identifying and addressing these streams individually, cities can divert more waste from landfills and create a circular economy that repurposes valuable resources.
Understanding MSW stream composition is crucial for developing effective municipal solid waste management strategies that address each component’s unique characteristics.

1. The Food Waste Stream
From Kitchen Scraps to Climate Concerns
Food waste is one of the largest contributors to landfills and incineration facilities.
The Impact of Food Waste
When food is wasted, so are the resources used to produce, transport, and distribute it. Decomposing food in landfills releases methane, a 28 times more potent greenhouse gas than CO₂, exacerbating climate change.
2. The Plastic Waste Stream
A Growing Waste Management Challenge
Plastics have revolutionized modern life—but they also pose one of the biggest environmental challenges.
Global plastic production has surged from 2 million tons in the 1950s to over 450 million tons today, yet only a fraction of plastics are effectively recycled.
The Impact of Plastics
While some are recyclable, contamination issues and inadequate processing infrastructure, like misunderstanding recycling symbols, result in many ending up in landfills or the environment. Over time, plastics break down into microplastics, which can get into waterways, soil, and food sources, impacting ecosystems and human health.
Most plastics pose a special problem in the waste stream because they are designed for durability, making them resistant to the natural decomposition process.

3. The Organic Waste Stream
Nature's Cycle or a Landfill Burden?
Many often overlook organic waste—including yard debris, textiles, and paper products—despite its strong potential to be repurposed.
The Impact of Organic Waste
Without proper diversion, decomposing organic waste contributes to landfill overcrowding, releases methane emissions, and poses risks to soil and water quality. However, by investing in smart infrastructure like anaerobic digestion systems, cities can convert organic waste into renewable fuels and valuable byproducts, supporting clean energy initiatives, agriculture, and greener urban spaces.
4. The Packaging Waste Stream
Balancing Convenience and Waste Management
Single-use packaging has surged with e-commerce, takeout services, and consumer demand for convenience, leading to an overwhelming volume of waste.
The Impact of Packaging Waste
Much of this waste isn’t easily recyclable, ending up in landfills or polluting waterways. Producing packaging materials consumes vast amounts of resources, including water, energy, and raw materials, further straining environmental sustainability.
5. The Hazardous Waste Stream
Handling Materials with Special Requirements
From electronics and household chemicals to industrial byproducts, hazardous waste requires careful disposal to prevent contamination.
The Impact of Hazardous Waste
Hazardous waste presents a unique challenge, and improper disposal of these materials can leach into soil and waterways, introducing toxic substances like lead and mercury into the environment.
As E-waste continues to rise, cities should address hazardous waste effectively, which demands stricter regulations, expanded recycling programs, and increased public awareness to ensure safer and more responsible disposal practices.
The Rising Types of Waste Volumes in Cities
The challenges of MSW management involve not only the sheer volume of waste but also the complexity of the waste streams, regulatory pressures, and inefficient resource utilization.
Electronic Waste
E-waste is the fastest-growing waste category, driven by shorter product life cycles and increasing consumer electronics demand.
Despite proper disposal guidelines, improper handling leads to toxic materials contamination and is the leading cause of fire in recycling centers and landfills.
The Impact of Single-Use Plastics and Packaging
Beyond E-waste, single-use plastics and disposable packaging continue to overwhelm waste management systems, straining landfills and recycling facilities.

The Role of Food and Organic Waste
Food waste remains one of the most underutilized resources in municipal waste systems. Investing in composting and waste-to-energy solutions can help reduce emissions while recovering valuable organic materials for biogas production and soil amendments.
Limitations and Challenges of Traditional Waste Management
Your cities rely on one or a combination of four primary waste management methods, and each comes with its challenges.

1. Landfills
While designed to contain and isolate waste, they pose significant environmental and logistical challenges. With limited space and growing waste volumes, many are reaching capacity, leaving municipalities scrambling for alternatives.
Limitations:
- Methane Emissions: Significant contributors to climate change.
- Leachate Contamination: Risk of groundwater pollution.
- Long-Term Land Use: Once filled, landfills remain unusable for decades.

2. Incineration
Incineration is a widely used method for waste disposal that involves burning waste materials at high temperatures to reduce volume and generate energy, but its efficiency depends on facility design.
Limitations:
- Air Pollution: Can release harmful emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy recovery varies by facility.

3. Recycling
Recycling reduces demand for virgin materials, but its effectiveness is limited by inconsistent processing capabilities and contamination issues.
Limitations:
- Material Degradation: Some materials lose quality over time and can’t be recycled again.
- High Costs: Sorting and processing require significant investment.
- Limited Markets: Demand for recycled materials fluctuates.

4. Composting
Composting can transform organic waste into a valuable resource, but it requires proper infrastructure.
Limitations:
- Public Awareness: Education is needed to encourage participation.
- Infrastructure: Collection and processing require funding.
Advanced MSW Processing Technologies Beyond Traditional Methods
The complexity of these diverse waste streams calls for sophisticated processing technologies that can handle multiple material types simultaneously. Modern MSW processing technologies integrate mechanical separation, biological treatment, and resource recovery systems to maximize material recovery while minimizing landfill dependency.
Mechanical Separation Technologies
Advanced mechanical separation systems use multiple technologies to sort mixed waste streams:
- Optical Sorting: Uses infrared and visual recognition to separate plastics by type and color
- Magnetic Separation: Removes ferrous metals from mixed waste streams
- Eddy Current Separation: Recovers non-ferrous metals like aluminum
- Air Classification: Separates lightweight materials from heavy organics
- Screen Separation: Sorts materials by size for downstream processing
Biological Processing Systems
Organic waste streams require specialized biological processing technologies:
- Anaerobic Digestion: Converts organic waste into biogas and digestate under oxygen-free conditions
- Composting Systems: Aerobic decomposition for creating soil amendments
- Hybrid Bio-Processing: Combines multiple biological treatment methods for optimal resource recovery
The most effective MSW processing technologies combine multiple systems to handle diverse waste streams comprehensively, addressing the fundamental challenge of municipal solid waste management: material heterogeneity.
Traditional waste management methods must adapt to meet rising urban waste challenges. Cities need scalable, cost-effective solutions that enhance resource recovery, reduce landfill overflow, and improve overall waste efficiency.
What Makes BurCell® Different?
- Optimized Waste Processing: Converts MSW into reusable materials, reducing your city’s landfill dependency by up to 75%.
- Lower Environmental Footprint: Cuts greenhouse gas emissions while maximizing material recovery for long-term municipal benefits.
- Cost-Effective Municipal Partnership: Adaptable for municipalities of all sizes, delivering measurable cost savings and regulatory compliance.
By implementing BurCell®’s innovative waste system, your city can transform waste challenges into community opportunities, improving environmental stewardship while strengthening economic resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions About MSW Management
What makes muncipal solid waste different from other waste types?
MSW contains diverse waste streams from multiple sources (residential, commercial, institutional) and requires different collection, processing, and disposal methods than uniform industrial waste.
How does MSW stream composition vary by location?
Urban areas typically generate more packaging and electronic waste, while suburban communities produce more yard waste and food scraps, requiring tailored management approaches.
What are the most effective municipal solid waste solutions?
Integrated approaches combining source reduction, recycling, composting, and advanced processing technologies like the BurCell® system provide the most comprehensive MSW management.
Why is MSW recycling challenging?
Contamination between different materials, varying local recycling capabilities, and fluctuating markets for recycled materials make MSW recycling more complex than single-stream waste processing.
How to Correctly Recycle Plastic Bottles: A Comprehensive Guide
Millions of plastic bottles are used worldwide every year, but only a fraction are recycled correctly.
Learning how to recycle plastic bottles not only conserves resources but also triggers a cascade of environmental and economic benefits.
This guide delves deep into the journey of a plastic bottle from your recycling bin to a new life, emphasizing why proper recycling is more than just a civic duty—it’s a critical step towards a sustainable future.
Understanding Plastic Bottle Recycling
Plastic bottles come in various types, each identified by a resin identification code found typically on the bottom.
The most common types include PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene).
PET is widely used for soft drinks and water bottles, while HDPE is used for sturdier containers like milk jugs or laundry detergents.
Recycling plastic bottles helps mitigate the effects of harmful chemicals and greenhouse gases released during production and decomposition.
Economically, recycling creates up to 6 times more jobs than landfill management, offering a significant boost to the economy.
Recycled PET and HDPE plastics are highly sought-after commodities in the manufacturing of textiles and automotive parts, making recycling economically beneficial beyond just environmental savings.
Preparing Plastic Bottles for Recycling
Cleaning and Sorting
Properly preparing plastic bottles for recycling involves more than just tossing them into a bin.
Bottles should be rinsed and dried to remove residual contents since contamination can render large batches of recyclables unprocessable.
Removing caps and labels is crucial as these can often be made of different types of plastics or materials that are not recyclable.
Sorting by Type
Sorting plastic bottles by type is crucial for effective recycling.
This often depends on local facilities' capabilities, but separating PET from HDPE can significantly increase the efficiency of recycling processes.
Misplaced plastics can contaminate the recycling stream, proving costly and counterproductive.
Recycling Process Explained
Collection and Transportation
Recycle plastic bottles begin their recycling journey at local collection centers from where they are transported to larger recycling facilities.
This transportation is often a complex logistical operation, designed to maximize efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
Processing Techniques
Once at the recycling plant, bottles are shredded into small pieces. These pieces are then washed and melted to form pellets, which can be used to make new plastic products.
Advanced techniques, such as chemical recycling, are emerging to break down plastics back into their original monomers, offering paths to recycle plastics that were previously non-recyclable.
Challenges in Plastic Bottle Recycling
Contamination Issues
Contamination remains a significant challenge in recycling plastic bottles. Food waste, incorrect plastics, and other materials can contaminate entire batches.
The impact of small label fragments and glue residue can degrade the quality of recycled plastic.
Market Challenges
The recycling market is highly susceptible to global supply and demand fluctuations. Prices for recycled plastics can vary, affecting the profitability and sustainability of recycling operations.
Economic incentives and technological advancements are critical to stabilizing the recycling market.
Technological Limitations
Current recycling technologies cannot handle all plastics, and innovations are essential to expand recycling capabilities.
For instance, multi-layered or colored plastics often pose recycling challenges due to their complex compositions, which make them more difficult to process efficiently.
How to Participate Effectively in Recycling Programs
Local Recycling Guidelines
To recycle plastic bottles effectively, it's crucial to understand and adhere to local recycling guidelines.
These regulations vary widely between regions and can significantly impact the recycling process.
Improving Household Recycling Practices
Improving recycling practices at the household level starts with education. Knowing what can and cannot be recycled in your locale is essential.
Engaging in community programs and advocating for better recycling facilities also play a crucial role.
Community Involvement
Community involvement can dramatically increase the rate of recycling.
Programs encouraging recycling through rewards or recognition can motivate residents to participate more diligently in recycling efforts.
Innovations and Future of Plastic Recycling
Emerging Technologies
Innovations such as enzymatic recycling, where enzymes break down plastics into their constituent chemicals, are pioneering.
These technologies could revolutionize the recycling industry by allowing for the recycling of previously non-recyclable plastics.
Sustainability Initiatives
Across the globe, initiatives to improve the sustainability of plastic recycling are gaining momentum.
For example, some companies are developing biodegradable plastics and improving the recyclability of plastic products from the design phase.
How Consumers Can Drive Change
Consumer demand for recycled products can drive significant change in the industry.
Consumers can make a substantial impact by opting for products made from recycled materials and supporting businesses that prioritize sustainability.
Conclusion
The proper recycling of plastic bottles is not just an environmental concern but a social responsibility that affects economic stability and sustainability.
Understanding the challenges and engaging in correct recycling practices empowers us all to contribute to a more sustainable future.
If you're looking to enhance your waste recycling efforts, consider reaching out to BurCell.
Contact us to see how we can help you succeed with waste recycling and turn your environmental responsibilities into actionable results.
How to Recycle Shredded Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
Shredded paper differs from whole sheets of paper in two main ways: fiber length and sorting difficulty.
When paper is shredded, its fibers become significantly shorter. This weakens the material and limits its ability to be recycled into new high-quality paper products.
Short fibers are harder to repurpose, often relegating shredded paper to low-grade recycled materials such as egg cartons or insulation.
Moreover, because shredded paper is so small, it often slips through the sorting machinery at recycling facilities.
Many Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs) rely on conveyor belts and rotating screens to separate recyclables.
Shredded paper can easily fall through these screens, mixing with non-paper recyclables or clogging the system.
Contamination Risks
Another major issue is contamination. Shredded paper is lightweight and can absorb moisture, food particles, or other contaminants.
If it mixes with non-recyclable materials, it may render entire batches of recyclables unusable. This is why many recycling centers have strict rules regarding shredded paper disposal.
Local Recycling Rules
Different municipalities have different rules about shredded paper. Some allow it in curbside recycling if it’s in paper bags, while others require it to be dropped off at specific locations
Always check with your local recycling facility to confirm their guidelines before disposing of shredded paper.
Step-by-Step Guide to Recycling Shredded Paper
Step 1: Confirm Local Recycling Guidelines
Before tossing shredded paper into the recycling bin, research your local waste management policies.
Many cities provide online resources that outline what materials are accepted in curbside programs. You can also call your local recycling center for clarification.
Step 2: Choose the Right Bag or Container
Some municipalities accept shredded paper in paper bags to prevent it from scattering during collection.
Unlike plastic bags, paper bags are recyclable and biodegradable, making them an environmentally friendly choice.
If your local program doesn’t accept shredded paper in curbside bins, consider taking it to a drop-off location.
Step 3: Secure the Shredded Paper Properly
To prevent shredded paper from becoming litter, always ensure it is contained. If allowed, place it in a paper bag and fold the top securely.
Avoid using plastic bags unless specifically directed by your recycling facility.
Step 4: Drop-Off or Curbside Collection
If curbside recycling is not an option, look for drop-off centers that accept shredded paper.
Many office supply stores, community centers, and local events offer free shredding services that ensure the paper is properly recycled.
Additionally, some recycling programs allow businesses to schedule bulk shredded paper pickups.
Alternative Ways to Reuse Shredded Paper
If recycling shredded paper proves difficult, consider repurposing it instead. Here are some creative and eco-friendly ways to give shredded paper a second life:
Composting
Shredded paper makes an excellent carbon source for composting. Since it’s high in carbon, it balances the nitrogen-rich food scraps in a compost pile.
However, avoid using glossy or ink-heavy paper, which can contain harmful chemicals. Mix shredded paper with kitchen scraps and garden waste to create nutrient-rich compost for your plants for best results.
Packing Material
Rather than using bubble wrap or foam peanuts, shredded paper is a sustainable alternative for packaging fragile items.
It provides cushioning and helps prevent damage during shipping. Businesses can also adopt this method to reduce reliance on plastic-based packing materials.
Pet Bedding and Litter
Small animals like guinea pigs, hamsters, and rabbits can benefit from shredded paper as bedding material.
It’s soft, absorbent, and easy to replace. When using shredded paper for pets, ensure that it is free from glossy coatings or toxic ink to keep them safe.
DIY Craft and Gardening Uses
- Paper Mache: Shredded paper can be turned into paper mache for arts and crafts projects.
- Mulch: In gardens, shredded paper can act as a mulch to retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
- Firestarter: Dry shredded paper can be used as an eco-friendly firestarter in fireplaces and outdoor fire pits.
Sustainable Shredding and Paper Reduction Strategies
Choose the Right Shredding Method
Not all shredding is equal. Cross-cut shredders produce finer pieces, which are harder to recycle, while strip-cut shredders create larger strips that are easier to manage.
If security concerns allow, opt for strip-cut shredding to improve recyclability.
Go Digital to Reduce Paper Waste
One of the best ways to minimize the need for shredding is to reduce paper usage altogether. Switching to digital documents, e-billing, and cloud storage significantly reduce paper waste.
Encourage workplaces to adopt paperless policies and use electronic signatures instead of printed contracts.
Use Secure Shredding Services with Eco-Friendly Disposal
Many professional shredding services partner with recycling companies to ensure that shredded paper is processed correctly.
Look for services that explicitly mention their commitment to sustainability.
Conclusion
While shredded paper presents unique challenges in the recycling process, understanding how to recycle it properly can make a significant environmental impact.
Always check local recycling guidelines, secure shredded paper appropriately, and consider alternative uses like composting or packing material.
The best strategy? Reduce your paper consumption from the start. Opt for digital solutions, choose sustainable shredding methods, and support companies that prioritize recycling.
Small changes in how we handle shredded paper can lead to a more sustainable future—one recycled sheet at a time.
Looking for a more effective way to handle waste recycling? Contact BurCell today to see how our innovative solutions can help you turn waste into valuable resources and contribute to a cleaner, greener planet.
What Is Food Waste and Why Should We Care About It?
In a world where resources are becoming increasingly scarce, understanding the full scope of "what is food waste" is more important than ever.
Food waste refers to any food fit for human consumption that gets discarded, whether at the retail, consumer, or supply chain level.
But the food waste story runs much more profound, touching every aspect of our economy, environment, and society.
In this article, we’ll explore how food waste impacts our world and why reducing it could be one of the most effective actions to preserve our planet and create a more sustainable future.
What Is Food Waste?
Food waste occurs when edible food is discarded at any stage in the food supply chain. It is crucial to distinguish between food waste and food loss
Food loss primarily happens during the production, post-harvest, and processing stages, while food waste occurs further along the supply chain, mainly during retail and consumption.
For example, when grocery stores discard produce that appears blemished or less aesthetically pleasing, or when households throw away food that has passed its "best before" date even though it is still safe to eat, that is considered food waste.
This phenomenon is much more prevalent than many realize. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately 1.3 billion tons of food are wasted every year globally.
To put that in perspective, this accounts for nearly one-third of all food produced for human consumption.
With food waste contributing heavily to economic inefficiencies, environmental degradation, and social injustices, its ripple effect is felt globally.
The Different Types of Food Waste
Food waste manifests in various ways, from households to retailers to supply chains.
Here are some of the most common categories of food waste:
- Household Food Waste: This type of waste typically occurs when consumers purchase more food than they need, misunderstand expiration dates, or improperly store food, causing it to spoil.
- Retail and Restaurant Waste: Supermarkets, restaurants, and food service providers often discard food due to overstocking, unsold items, or plate waste.
- Supply Chain Waste: This type of waste occurs during production, transportation, and storage. Losses happen due to improper storage conditions, transportation delays, and mechanical issues.
Understanding the nuances of food waste is critical in developing targeted strategies to reduce its impact.
Why Should We Care About Food Waste?
The question is not just "what is food waste?" but why it matters. The effects of food waste extend beyond landfills.
It has profound implications for the environment, economy, and society at large.
Environmental Impact
When food is wasted, the resources used to produce that food—water, energy, labor, and land—are also wasted.
Even more concerning is food waste's significant impact on climate change.
As food decomposes in landfills, it releases methane, a greenhouse gas approximately 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide, in trapping heat in the atmosphere.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), food waste is the single largest component of municipal solid waste (MSW) in the United States, accounting for 24% of landfill inputs.
The problem is that landfills are rapidly reaching capacity and contribute significantly to methane emissions, exacerbating the climate crisis.
Another lesser-known impact of food waste is deforestation. Vast areas of forested land are cleared to make room for agriculture.
When the food produced on this land is wasted, the natural ecosystems displaced for farming suffer unnecessarily.
The FAO estimates that around 30% of the world’s agricultural land is used to grow food that is ultimately wasted.
Economic Impact
The financial costs associated with food waste are staggering. In the United States alone, it is estimated that $218 billion worth of food is wasted annually.
This translates into about $1,500 per year for the average family of four. On a global scale, food waste represents a $1 trillion loss to the economy annually.
For businesses, especially those in the retail and hospitality industries, food waste creates inefficiencies that eat away at profit margins.
Companies that fail to manage inventory effectively discard significant amounts of unsold food, resulting in a direct financial loss and incurring costs related to waste management.
Social Impact
In a world where 811 million people go hungry every day, the issue of food waste takes on a profound ethical dimension.
The food wasted in industrialized countries could feed the world's hungry multiple times.
Addressing food waste could play a pivotal role in reducing global hunger and improving food security.
Moreover, wasting food contributes to economic inequality. Wealthier nations and communities overproduce and discard food, so poorer areas are left to cope with limited resources.
This stark contrast reveals the moral obligation to manage food sustainably and equitably.
Global Food Waste Statistics
The scale of global food waste can be hard to fathom, but the numbers clearly show the problem’s enormity. Each year:
- Europe and North America waste an estimated 95-115 kg per person.
- Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia waste only about 6-11 kg per person, but they experience higher rates of food loss during production and transportation.
While industrialized countries waste more at the consumer level, developing nations experience food loss earlier in the supply chain due to inadequate infrastructure and preservation technologies.
This global disparity reveals the need for effective region-specific solutions to combat food waste.
The Environmental and Health Benefits of Reducing Food Waste
Tackling food waste offers a range of environmental and health benefits.
Reducing waste would not only lessen the amount of methane emissions but also conserve natural resources, such as water and energy, used in food production.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Given that food waste in landfills contributes significantly to methane production, a concerted effort to reduce food waste could have a meaningful impact on slowing climate change.
According to Project Drawdown, reducing food waste is one of the top three solutions for reversing global warming.
Saving Natural Resources
Food production requires vast amounts of water, energy, and land. For example, it takes approximately 1,800 gallons of water to produce just one pound of beef.
By reducing food waste, we can significantly reduce these resource expenditures, preserving precious natural resources for future generations.
Healthier Communities
Redirecting edible food that would otherwise be wasted to needy communities is one of the simplest ways to improve food security and promote public health.
Food recovery organizations, such as Feeding America, have pioneered programs that redistribute surplus food from grocery stores, restaurants, and farms to those in need.
How to Prevent Food Waste
So, what can be done to prevent food waste? It requires action from all levels of society, from individuals to businesses to governments.
Here are some ways that food waste can be reduced:
For Individuals
At the household level, food waste can be reduced by making small changes in behavior.
For instance:
- Meal Planning: Plan meals ahead of time to avoid over-purchasing.
- Understanding Expiration Dates: Many people throw away food once it reaches its "sell by" or "best before" date, even though it is still safe to eat. Understanding the difference between these terms can help reduce unnecessary waste.
- Proper Food Storage: Storing food correctly can prolong its shelf life. For example, refrigerating fruits and vegetables at the right temperature can prevent spoilage.
For Businesses
Businesses have a critical role to play in food waste reduction.
Technology solutions that help manage inventory, track expiration dates, and optimize supply chain logistics can make a significant difference.
Additionally, many businesses partner with organizations that redistribute surplus food, such as food banks and shelters.
- Composting and Recycling Programs: Businesses can implement composting and recycling programs to divert organic waste from landfills.
How Food Waste Can Be Turned Into Energy
One of the most exciting innovations in food waste management is converting food waste into energy.
This process, known as anaerobic digestion, involves breaking down organic materials, such as food waste, in an oxygen-free environment to produce biogas, a renewable energy source.
One company in charge of turning food waste into energy is BurCell Technologies.
Their BurCell® System is a groundbreaking platform designed to recover valuable organics from Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) streams.
This system not only diverts up to 75% of waste from landfills but also recovers 90% of organics trapped in waste streams.
By enhancing the digestibility of the organic fraction of food waste, the BurCell® System makes it easier to feed this material into anaerobic digesters.
This results in more predictable and sustained biogas production, offering a higher energy yield over a shorter processing time.
In addition to producing energy from food waste, the BurCell® System also enables the recovery of mixed plastics and other high-BTU materials for thermal conversion.
Its modular design offers a cost-effective solution for waste processing, making it an attractive option for municipalities and businesses looking to reduce waste while generating energy.
The Role of BurCell® System in Tackling Food Waste
The BurCell® System provides a revolutionary approach to food waste management.
Unlike traditional waste processing centers, it focuses on enhancing the digestibility and recovery of organics, maximizing the potential to turn waste into energy.
Enhancing Digestibility
The BurCell® System makes it easier to process in anaerobic digesters by breaking down the organic fraction of food waste.
This increases biogas production and shortens the hydraulic residence time, meaning less time is needed to produce the same or more energy.
Maximizing Organic Recovery
BurCell® can recover over 90% of valuable organics from MSW streams.
This ensures that more food waste can be repurposed rather than being sent to landfills, where it would contribute to methane emissions.
A Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to traditional waste processing centers, the BurCell® System’s modular design reduces daily operation costs.
It is a viable and sustainable option for businesses and communities looking to implement waste-to-energy solutions.
Government Initiatives and Policies
Reducing food waste has become a top priority for many governments worldwide.
Legislation and initiatives, such as food waste bans and landfill restrictions, have been introduced to encourage more sustainable waste management practices.
In the United States, the EPA’s Food Recovery Hierarchy prioritizes reducing food waste through prevention, donation, and recycling before landfilling.
Additionally, the United Nations has set a goal to reduce food waste by 50% by 2030 as part of its Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Conclusion
Food waste is a complex issue that affects every aspect of our lives—from the environment to the economy and social well-being.
By understanding what food waste is and the significance of reducing it, we can make more informed choices and take meaningful actions to mitigate its impacts.
Whether through personal efforts, business initiatives, or adopting innovative solutions like the BurCell® System, reducing food waste offers long-lasting benefits for our planet.
If you’re ready to explore how food waste recycling can make a difference for your community or business, contact BurCell Technologies today.
Let us help you succeed with cutting-edge solutions to transform waste into valuable resources and energy.
Together, we can build a more sustainable future.
FAQs
What is food waste?
Food waste refers to any edible food that is discarded or lost before it can be consumed. This can happen at various stages, including production, processing, distribution, and consumption.
Why should we care about food waste?
Reducing food waste is important for several reasons. It helps conserve resources like land, water, and energy that are used to produce food. Additionally, food waste contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, which negatively impacts the environment.
Where does most food waste occur?
A significant portion of food waste happens at the consumer level. Households often discard leftover food or purchase more than they need, leading to unnecessary waste. However, food waste also occurs at the agricultural, processing, and retail levels.
What are the environmental consequences of food waste?
Food waste contributes to climate change by releasing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, when it decomposes in landfills. It also wastes valuable resources like water and energy that are used in food production.
How can I reduce food waste at home?
There are many ways to reduce food waste at home. This includes planning meals, storing food properly, using leftovers creatively, and composting food scraps. Additionally, supporting local farmers and reducing food packaging can also help minimize waste.
The Alarming Reality of Food Waste in America: Causes and Solutions
Food waste in America is an alarming issue that not only impacts our environment but also our economy and society as a whole.
In a country where millions of people struggle with hunger daily, the sheer volume of food in landfills is staggering.
The paradox of abundance and waste reflects a broken system that requires immediate attention and action.
This article delves deep into the causes of food waste in America. It explores innovative solutions that could turn this waste into valuable resources, benefiting both the planet and its people.
The Scope of Food Waste in America
Food waste is not just an isolated problem but a widespread issue with far-reaching consequences.
In the United States, approximately 40% of all food produced is never consumed, amounting to nearly 133 billion pounds of food wasted annually.
To put this into perspective, this wasted food could feed the entire California and New York population combined.
The statistics surrounding food waste in America are both shocking and disheartening.
According to the USDA, food waste is the single most significant component of municipal solid waste in the United States, with more than 63 million tons of food discarded yearly.
This waste occurs at every stage of the food supply chain—from farms to retail outlets to households.
While food waste is a global issue, the United States ranks as one of the worst offenders. In comparison to other developed countries, Americans waste more food per capita.
Cultural factors, such as the preference for perfect-looking produce and the tendency to over-purchase, contribute to the high levels of waste.
In contrast, countries like France have implemented strict regulations that reduce food waste, such as banning supermarkets from discarding unsold food and requiring them to donate it to charity.
Causes of Food Waste in America
Understanding the root causes of food waste in America is essential to finding practical solutions.
The issue is complex, involving multiple stages of the food supply chain and various stakeholders, from farmers to consumers.
1. Agricultural Practices
At the beginning of the food supply chain, agricultural practices play a significant role in food waste.
Overproduction is a common issue driven by market demands and the unpredictability of crop yields.
Farmers often produce more than necessary to ensure they meet contracts, leading to a surplus that may never be harvested or sold.
Additionally, losses during harvesting and transportation, often due to inadequate infrastructure or poor handling, further contribute to the waste.
2. Retail and Consumer Behavior
Retail practices also significantly impact food waste in America.
Supermarkets and retailers often set strict aesthetic standards for produce, leading to the rejection of perfectly edible fruits and vegetables that do not meet visual criteria.
This "perfect produce" phenomenon results in tons of food being discarded before reaching store shelves.
Consumer behavior exacerbates the problem. Many Americans purchase more food than they can consume, often driven by marketing tactics such as bulk sales and the perceived value of buying in larger quantities.
Also, confusion over expiration dates leads to premature disposal of food that is still safe.
According to a Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) report, up to 90% of Americans misinterpret date labels, leading to unnecessary waste.
3. Food Service Industry
The food service industry, including restaurants and catering services, contributes to food waste.
Over-preparation is a common practice, with large portions often served to meet customer expectations or to prevent the perception of scarcity.
However, this leads to a significant amount of uneaten food being discarded.
Moreover, the lack of efficient food management systems in many establishments means that food nearing its expiration date is often thrown away rather than being donated or repurposed.
4. Household Waste
Household waste accounts for the most significant portion of food waste in America.
The primary culprits are misplanning, overbuying, and a lack of awareness about proper food storage.
Many households are unaware of how to store food to extend its shelf life or simply forget about perishables until they spoil.
Additionally, the modern lifestyle, emphasizing convenience and fast food, often results in leftovers being ignored and eventually discarded.
The Impact of Food Waste
The consequences of food waste in America are far-reaching, affecting the environment, economy, and society.
Addressing food waste is about reducing waste and creating a more sustainable and equitable food system.
1. Environmental Impact
Food waste has a profound impact on the environment. When food is wasted, all the resources used to produce it—including water, energy, and land—are also wasted.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), food waste accounts for approximately 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Food waste decomposes anaerobically in landfills, producing methane, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change.
Moreover, the production of food that ultimately goes to waste strains our natural resources.
Agriculture is one of the largest consumers of freshwater; when food is wasted, the water used in its production is also lost.
The same applies to the energy and land resources used to grow, harvest, and transport food.
2. Economic Impact
The economic cost of food waste in America is staggering. The USDA estimates that food waste costs the United States approximately $161 billion annually.
This includes the cost of producing, processing, and disposing of never consumed food.
Food waste represents a significant loss of potential revenue for businesses, while for consumers, it translates to wasted money that could be better spent on other necessities.
Food waste also impacts food prices and availability. When food is wasted, the supply is effectively reduced, increasing prices and limiting access to affordable food for low-income families.
This is particularly concerning given that millions of Americans struggle with food insecurity.
3. Social and Ethical Implications
Food waste's social and ethical implications in America are perhaps the most troubling.
The juxtaposition of food waste and hunger is a stark reminder of the inequality in our food system.
While millions of tons of food are discarded each year, approximately 35 million Americans, including 10 million children, experience food insecurity.
Food waste is not just an economic and environmental issue but also a moral one.
The ethical responsibility to reduce food waste is clear: by wasting less food, we can ensure that more people have access to the nourishment they need.
This is not only a matter of charity but also of creating a more just and equitable society.
Solutions to Food Waste
While the problem of food waste in America is daunting, there are a variety of solutions that can help reduce waste and turn it into a valuable resource.
These solutions involve government intervention, technological innovation, business practices, and consumer education.
1. Government and Policy Interventions
Government policies play a crucial role in addressing food waste. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the need for legislation to reduce food waste at all levels of the supply chain.
The U.S. government has set a goal to cut food waste in half by 2030, aligning with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals.
One effective policy intervention is the implementation of food waste regulations, such as those seen in France.
The French government has banned supermarkets from throwing away unsold food, requiring them to donate it to charities.
Similar policies could be adopted in the United States to encourage food donation and reduce waste at the retail level.
Support for food donation programs is another critical area of government intervention.
Tax incentives for businesses that donate food and grants for organizations that facilitate food redistribution can ensure that surplus food reaches those in need rather than end up in landfills.
2. Innovations in Food Management
Technological innovation is critical to reducing food waste in America.
Advances in food management, including apps and software for inventory tracking, can help businesses and consumers alike reduce waste.
For example, apps like "Too Good To Go" connect consumers with restaurants and stores offering surplus food at discounted prices, thereby preventing waste and providing affordable meals.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also used to optimize food supply chains. AI algorithms can predict demand more accurately, reducing the likelihood of overproduction and waste.
Additionally, innovations in food preservation, such as vacuum sealing and advanced refrigeration technologies, can extend the shelf life of perishable items, reducing the risk of spoilage.
3. Role of Businesses and the Private Sector
The private sector has a significant role to play in reducing food waste. Businesses that adopt sustainable practices can reduce waste and improve their bottom line.
For example, restaurants implementing portion control, menu planning, and efficient inventory management can reduce waste and save money.
Successful case studies of food waste reduction in the private sector highlight the potential for change.
For instance, Tesco's supermarket chain has implemented a food waste reduction program that includes donating surplus food, improving inventory management, and educating consumers about food storage and preparation.
As a result, Tesco has significantly reduced its food waste and set an example for other retailers to follow.
4. Consumer Education and Awareness
Educating consumers about food waste is crucial to reducing waste at the household level.
Simple tips like meal planning, proper food storage, and understanding expiration dates can help consumers reduce waste and save money.
For example, storing fruits and vegetables in the appropriate refrigerator sections can extend their shelf life, while freezing leftovers can prevent them from going to waste.
Understanding food labels is another crucial aspect of consumer education.
The confusion surrounding "best by," "use by," and "sell by" dates leads many consumers to discard food prematurely. Educating consumers about the meaning of these labels can reduce unnecessary waste.
How Waste Could Be Turned Into Energy
In addition to reducing waste, there is significant potential to turn food waste into energy, transforming a problem into a resource.
Waste-to-energy systems, such as those enabled by the BurCell® System technology, offer a promising solution.
Organic waste, including food waste, represents a vast untapped resource.
With 133 billion pounds of food wasted annually in the U.S., there is a significant opportunity to repurpose this material through recycling and waste-to-energy systems.
The BurCell® System is a cutting-edge technology that converts organic waste into energy through anaerobic digestion.
This process involves using microorganisms to break down and convert organic waste into biogas, biodiesel, or ethanol. The final product can then be used to generate electricity or fuel vehicles.
Anaerobic digestion offers a sustainable and carbon-neutral solution to waste management.
Unlike fossil fuels, which release carbon that has been sequestered for millions of years, biogas is produced from materials that have only recently absorbed carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
While anaerobic digestion does produce methane, a greenhouse gas, the carbon in the methane comes from recently absorbed carbon dioxide, making the process largely carbon-neutral.
The environmental benefits of using biogas and other fuels derived from anaerobic digestion are significant.
By converting food waste into energy, the BurCell® System reduces the need for fossil fuels and decreases greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, the process diverts waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions and the environmental impact of waste disposal.
The BurCell® System represents a shift towards a circular economy, where waste is not simply discarded but repurposed as a valuable resource.
This technology has the potential to revolutionize waste management and energy production, making it a key player in the fight against climate change.
The Role of Food Waste in the Circular Economy
The concept of a circular economy is central to addressing food waste in America.
In a circular economy, waste is not seen as an end product but as a resource that can be reused, recycled, or repurposed.
Food waste plays a critical role in this system, with the potential to be transformed into valuable resources such as compost, animal feed, or energy.
Composting and recycling food waste are essential components of a circular economy.
Composting converts organic waste into nutrient-rich soil, which can be used to improve agricultural productivity and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers.
Recycling food waste into animal feed provides a sustainable source of nutrition for livestock, reducing the demand for other feed sources.
Biogas production and energy recovery are also essential aspects of a circular economy.
As mentioned earlier, the BurCell® System is a prime example of how food waste can be converted into energy, providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels and reducing the environmental impact of waste disposal.
Conclusion
The issue of food waste in America is both a challenge and an opportunity. While the statistics are alarming, the potential for change is significant.
Understanding the causes of food waste and implementing innovative solutions can create a more sustainable and equitable food system.
Whether through government policy, technological innovation, business practices, or individual action, we can do much to reduce food waste and turn it into a valuable resource.
The time to act is now; together, we can make a difference.
If you're ready to take action and explore how food waste can be transformed into energy, contact BurCell today.
Let us help you succeed with cutting-edge food waste recycling solutions that reduce waste and contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.
FAQs
What is the primary cause of food waste in the United States?
The primary cause of food waste in the U.S. is overproduction and consumer waste. This means that too much food is produced or purchased, and much of it ends up in landfills.
How does food waste impact the environment?
Food waste contributes significantly to climate change due to the methane gas emitted when it decomposes in landfills. Additionally, the resources used to produce food, such as water and land, are wasted.
What are some solutions to reduce food waste?
Solutions to reduce food waste include improving food production and distribution practices, encouraging consumers to buy only what they need, and supporting initiatives to donate surplus food.
How can individuals help reduce food waste at home?
Individuals can help reduce food waste at home by planning meals, storing food properly, composting food scraps, and donating surplus food.
What role do businesses play in reducing food waste?
Businesses can play a significant role in reducing food waste by implementing practices such as donating surplus food, reducing food portion sizes, and using food waste to create new products.
The Importance of Proper Community Waste Disposal
In today's world, community waste disposal has become more than just a routine chore; it is a critical component of our environmental and public health strategies.
As we navigate through the complexities of urbanization, population growth, and the demands of modern life, the proper management of waste has taken on a new level of importance.
But what does "proper" really mean in this context? And why should communities care?
The answer lies in the profound impact that waste disposal has on both our environment and our health.
It’s not just about keeping our neighborhoods clean—it’s about preserving the ecosystems that sustain us and ensuring the well-being of the communities that call these ecosystems home.
The Environmental Benefits of Proper Waste Disposal
1. Reduction in Pollution
Pollution is a global issue with far-reaching consequences, from the air we breathe to the water we drink.
Proper community waste disposal plays a crucial role in reducing pollution by ensuring that waste is managed to minimize its release into the environment.
When waste is not correctly disposed of, it can end up in places it shouldn't—such as oceans, rivers, and forests.
This contaminates these natural habitats and disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems.
For example, plastic waste in oceans is notorious for harming marine life, leading to fish and other sea creatures ingesting plastic particles.
According to a study by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, it’s estimated that by 2050, there could be more plastic than fish in the oceans by weight.
Proper disposal methods, such as recycling and composting, help reduce the amount of waste in landfills or, worse, in our natural environments.
Recycling, in particular, helps reduce the need for raw materials, thereby lowering pollution levels associated with extracting and processing these materials.
2. Conservation of Natural Resources
One of the lesser-known benefits of proper waste disposal is its role in conserving natural resources.
When communities engage in recycling and composting, they contribute to the reduction of resource extraction activities, which are often environmentally destructive.
For instance, recycling paper reduces the need to cut down trees, thereby conserving forests and the biodiversity they support.
Similarly, recycling metals reduces the need for mining, which can devastate the environment, including deforestation, soil erosion, and water contamination.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) highlights that recycling aluminum, for example, saves 95% of the energy required to make the same amount of aluminum from raw materials.
3. Mitigating Climate Change
The connection between waste disposal and climate change is often overlooked.
However, proper waste management is vital to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Waste in landfills is a significant source of methane, a potent greenhouse gas 25 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide over 100 years.
By reducing waste sent to landfills, communities can significantly lower methane emissions.
Composting organic waste, for instance, not only diverts it from landfills but also converts it into valuable compost that can enrich soils and support sustainable agriculture.
4. Protection of Wildlife and Marine Life
Improper waste disposal is a silent killer of wildlife.
Animals, both on land and in the water, are often the victims of human negligence in waste management.
Birds, mammals, and marine creatures can ingest or become entangled in waste, leading to injury or death.
One particularly heartbreaking example is the plight of sea turtles, which often mistake plastic bags for jellyfish—a primary food source. Ingesting plastic can lead to blockages in their digestive systems, often resulting in death.
The Ocean Conservancy reports that 52% of the world’s sea turtles have ingested plastic.
By ensuring proper community waste disposal, we can protect wildlife from the dangers of waste pollution.
Moreover, communities that take proactive steps to manage their waste contribute to preserving biodiversity, which is essential for the health of our planet.
The Health Benefits of Proper Waste Disposal
1. Prevention of Disease
The connection between waste disposal and public health is well-documented yet often underappreciated.
Improper waste disposal can lead to the proliferation of pests and pathogens, increasing the risk of disease outbreaks.
For example, stagnant waste can become a breeding ground for mosquitoes, vectors for diseases such as malaria and dengue fever.
The health risks are even more pronounced in developing countries, where waste management infrastructure is often inadequate.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), exposure to improperly managed waste is associated with a range of health issues, including respiratory infections, gastrointestinal infections, and even more severe conditions like cholera.
Proper waste disposal practices help prevent the spread of these diseases by removing waste from environments where it can cause harm.
This is particularly important in urban areas, where population density increases the risk of disease transmission.
2. Improvement in Public Health
Communities that prioritize proper waste disposal also enjoy broader public health benefits.
Clean, waste-free environments contribute to overall well-being, reducing the incidence of health issues associated with poor sanitation.
This is especially important in densely populated areas where waste accumulation can quickly become a public health hazard.
For example, studies have shown that residents in areas with effective waste management systems report lower respiratory and gastrointestinal illness rates.
Clean environments also support mental health by reducing stress and anxiety associated with living in polluted or unsanitary conditions.
3. Reduced Risk of Hazardous Exposure
Another critical aspect of community waste disposal is the safe handling and disposal of hazardous waste.
This includes chemicals, medical waste, and other materials that can pose serious health risks if not properly managed.
Hazardous waste can contaminate soil and water supplies, leading to long-term health issues such as cancer, neurological disorders, and reproductive problems.
A notable case is the Love Canal incident in New York, where the improper disposal of chemical waste led to widespread health issues in the surrounding community, including birth defects and increased cancer rates.
Communities can protect their residents from these severe health risks by correctly disposing of hazardous waste.
This involves proper disposal and education on the safe handling of hazardous materials.
The Role of Technology in Modern Waste Management
Technology has revolutionized waste management, offering new ways to reduce, reuse, and recycle waste.
Innovations such as smart bins, waste-to-energy plants, and advanced recycling techniques make it easier for communities to manage their waste more effectively.
Smart bins, for example, are equipped with sensors that monitor the level of waste and notify waste management services when they need to be emptied.
This improves efficiency and helps prevent overflow and the associated health risks.
Additionally, waste-to-energy plants convert non-recyclable waste into electricity, providing a sustainable energy source while reducing waste sent to landfills.
While technology plays a crucial role in modern waste management, ensuring these practices are sustainable is equally important.
Sustainable waste management practices aim to minimize the environmental impact of waste disposal while maximizing resource recovery.
For example, zero-waste initiatives encourage communities to reduce their waste generation to the absolute minimum and send no waste to landfills or incinerators.
These initiatives often involve composting, recycling, and adopting circular economy principles, where waste materials are reused or repurposed rather than discarded.
How the Burcell® System Can Help
The Burcell® System represents a significant advancement in waste management, offering an innovative solution for processing waste materials more effectively.
Developed by BurCell Technologies, this system is designed to maximize the recovery of valuable resources from waste while minimizing the environmental impact.
1. Enhancing Waste Management Efficiency
One of the standout features of the Burcell® System is its ability to process a wide range of waste materials, including both organic and non-organic waste.
The system is modular and scalable, making it suitable for use in communities of all sizes.
By enhancing the efficiency of waste processing, the Burcell® System helps reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, contributing to the overall sustainability of community waste disposal efforts.
2. Turning Waste into Energy
A vital benefit of the Burcell® System is its ability to convert organic waste into energy.
Through a process known as anaerobic digestion, the system breaks down organic waste to produce biogas, which can be used to generate electricity.
This reduces the volume of waste and provides a renewable energy source, helping communities transition to more sustainable energy practices.
The Burcell® System also enhances the digestibility of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (MSW), making it easier to feed into an anaerobic digester.
This leads to a higher biogas yield over a shorter hydraulic residence time, providing a more sustained and predictable gas generation performance.
Steps Communities Can Take to Improve Waste Disposal
1. Education and Awareness
Education and awareness are among the most effective ways to improve community waste disposal.
By informing residents about the importance of proper waste disposal and the steps they can take to contribute, communities can foster a culture of responsibility and sustainability.
Community programs and initiatives focusing on waste reduction, recycling, and composting are essential for building this awareness.
Schools, local organizations, and government agencies can all play a role in educating the public and encouraging active participation in waste management efforts.
2. Infrastructure Development
Effective waste disposal requires the proper infrastructure.
This includes waste collection and processing facilities, recycling centers, composting sites, and hazardous waste disposal units.
Investing in this infrastructure is crucial for ensuring that waste is managed to minimize environmental and health impacts.
For example, communities can develop centralized recycling centers where residents can drop off recyclable materials.
Composting facilities can process organic waste, turning it into valuable compost that can be used to support local agriculture.
Additionally, hazardous waste disposal units ensure that dangerous materials are handled safely and do not pose a risk to public health.
3. Policy and Regulation
Local governments play a critical role in regulating waste disposal and enforcing policies that promote sustainability.
Effective waste management policies can include recycling regulations, waste reduction incentives, and penalties for improper disposal.
Case studies of successful waste management policies demonstrate the importance of government intervention in achieving community waste disposal goals.
For example, San Francisco’s zero-waste initiative, which mandates recycling and composting for all residents and businesses, has significantly reduced the amount of waste sent to landfills, setting a model for other cities to follow.
4. Encouraging Community Participation
Community participation is critical to the success of any waste management initiative.
Communities can ensure that these initiatives are more effective and sustainable by involving residents in the decision-making process and encouraging them to take an active role in waste disposal efforts.
Programs that promote community involvement, such as neighborhood cleanups, recycling drives, and composting workshops, can help build a sense of ownership and responsibility among residents.
These initiatives improve waste disposal practices, strengthen community bonds, and foster a culture of sustainability.
Conclusion
Proper community waste disposal is essential not just for keeping our streets clean—it's a vital aspect of protecting the environment and ensuring public health.
By reducing pollution, conserving resources, and preventing disease, the benefits of effective waste management extend far and wide.
As we move forward, integrating technology, education, and community engagement will be pivotal in evolving our waste management strategies.
Innovations like the Burcell® System are at the forefront of this transformation, offering efficient and sustainable solutions that enable communities to convert waste into valuable resources.
To enhance waste disposal practices in your community and contribute to a healthier, more sustainable future.
Contact BurCell today to discover how we can assist you in achieving superior waste disposal solutions. Together, we can make a significant difference.
FAQs
Why is proper waste disposal important?
Improper waste disposal can have negative consequences on both human health and the environment. It can lead to the spread of diseases, pollution of water sources, and harm to wildlife. Proper waste disposal helps to protect public health and the environment.
What are the different methods of waste disposal?
There are several methods of waste disposal, including recycling, composting, incineration, and landfilling. Recycling and composting are considered the most environmentally friendly methods, as they help to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
What are the benefits of recycling?
Recycling conserves natural resources, reduces pollution, and creates jobs. It also helps to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, which can help to protect the environment.
How can I help to reduce waste in my community?
There are many things you can do to help reduce waste in your community. You can recycle and compost, reduce your consumption of single-use items, and support businesses that are committed to sustainability.
What are the challenges of waste management in developing countries?
Developing countries often face challenges in managing waste due to lack of infrastructure, resources, and education. This can lead to improper waste disposal and environmental pollution.
Effective Food Waste Management: Strategies for Reducing Waste in Your Home
Food waste management is one of the most critical challenges facing households worldwide today.
Food waste is not only a financial burden but also an environmental one, contributing significantly to global greenhouse gas emissions.
According to the United Nations, around one-third of all food produced globally is wasted, amounting to about 1.3 billion tons of food per year.
For individual households, an estimated $1,500 worth of groceries goes to waste annually in the U.S. alone.
With such staggering numbers, effective food waste management at home is more important than ever.
This article will take you through strategies you can quickly implement to cut down on waste, reduce your carbon footprint, and save money, all while positively impacting the environment.
Understanding Food Waste at Home
To tackle the food waste problem, it's essential to understand its types and causes. Household food waste falls into two main categories: avoidable and unavoidable.
Types of Food Waste
- Avoidable food waste: This includes edible food at some point but went bad due to poor planning, improper storage, or simple neglect. For example, those bags of salad that go limp in the back of the fridge or the loaf of bread that molds before you even open it.
- Unavoidable food waste: These are inedible parts like eggshells, bones, and fruit peels, which are naturally disposed of.
Common Causes of Food Waste
- Over-purchasing: Often, we buy more than we need, especially with bulk shopping. This might seem cost-effective, but it often leads to excess food expiring before it can be used.
- Improper storage: Incorrect storage practices accelerate spoilage. A good example is refrigerating fruits that do better at room temperature.
- Neglecting leftovers: Many households overlook leftovers, leading to more waste.
Understanding these categories and causes is the first step in better food waste management.
But knowledge alone isn't enough. Let’s delve into practical strategies to implement in your household.
Planning and Shopping Wisely
An effective food waste management plan begins long before you enter the kitchen.
The decisions you make at the grocery store can significantly affect how much food goes to waste at home.
Meal Planning Tips
One of the simplest ways to reduce food waste is to plan your meals. This doesn’t have to be a complex process.
Start by deciding what you’ll eat for the week and create a meal plan. To avoid waste, include versatile ingredients that can be used across several meals, such as rice, beans, and chicken.
A pro tip is to focus on ingredients with a longer shelf life for most of your meals.
Canned vegetables, frozen foods, and grains can last longer than fresh produce, allowing more flexibility in your cooking schedule. Plus, these items are less likely to end up in the trash.
Creating a Shopping List
A strategic shopping list ensures that you buy only what you need.
Stick to your list as much as possible and avoid impulsive buys, particularly with perishable items prone to going bad quickly.
Not only does this cut down on waste, but it also saves money.
According to a Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) report, households that use a shopping list and stick to it can reduce food waste by up to 25%.
If you’re looking to manage food waste, discipline at the store is critical.
Buying in Appropriate Quantities
While bulk buying is tempting—thanks to the cost savings—it can lead to food spoilage if not managed correctly.
Instead of purchasing large quantities of perishable items like vegetables, fruit, and dairy products, consider replenishing smaller amounts as needed.
A general rule of thumb is only to buy what you can use within the next 7-10 days.
This method not only aids in food waste management but also ensures fresher, more flavorful meals. As the saying goes, "Fresh is best."
Proper Food Storage Techniques
Storing food correctly is one of the easiest yet most effective food waste management strategies.
Many people aren't aware that improper storage is a leading cause of spoilage. With a few simple changes, you can extend the life of your groceries.
Storing Fresh Produce
Different types of produce require different storage methods. Some fruits, like apples, do best in the refrigerator, while others, like bananas and tomatoes, fare better at room temperature.
Store leafy greens in a damp cloth or paper towel to keep them crisp, while herbs like cilantro and parsley can be stored in a glass of water like a bouquet.
A lesser-known tip is to separate ethylene-producing fruits like bananas and avocados from ethylene-sensitive items such as berries, as the gas can speed up ripening and lead to quicker spoilage.
Freezing Leftovers
The freezer is your best friend when it comes to reducing food waste. Almost any leftover food can be frozen, from soups and stews to bread and cooked meats.
Freezing leftovers not only reduces waste but also provides you with a quick meal option when you're short on time.
To prevent freezer burn, store food in airtight containers or freezer bags and label them with the date.
This way, you’ll know exactly what’s in your freezer and when it was stored.
Utilizing Airtight Containers
Investing in good quality, airtight containers is a game-changer.
These containers can help maintain the freshness of food for a longer period, especially for leftovers, grains, and pantry staples.
Clear containers also allow you to see what's inside, making it less likely for forgotten items to spoil at the back of your fridge.
Creative Ways to Use Leftovers
If you’re committed to food waste management, learning how to repurpose leftovers is crucial.
Leftovers don’t have to be boring—they can be transformed into entirely new meals with a bit of creativity.
Meal Prepping
Meal prepping is a great way to avoid wasting food. It involves cooking large quantities of a meal, portioning it out, and storing it for future use.
For instance, a roast chicken can be used in several dishes, such as chicken salads, sandwiches, and soups.
Batch Cooking and Freezing
Cooking large portions of food, like casseroles, chili, or pasta, and freezing them in individual servings is another intelligent way to ensure nothing goes to waste.
On busy days, simply reheat one of these meals instead of opting for takeout, reducing both food waste and expenses.
Food Waste Recipes
Specific recipes are designed to use food scraps or items that might otherwise be thrown away.
For example, you can turn overripe bananas into banana bread, stale bread into croutons, and vegetable scraps into broth.
Websites like Love Food Hate Waste offer a wide range of creative recipes that help minimize waste.
Composting: Turning Waste into Resource
Composting is an eco-friendly method of food waste management that transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich soil.
Not only does composting reduce landfill waste, but it also helps improve the quality of your garden soil.
What is Composting?
Composting is breaking down organic materials—like fruit and vegetable peels, coffee grounds, and eggshells—into compost.
This can then be used as a natural fertilizer for your garden. The process is a win-win: it reduces waste while creating a valuable resource for your plants.
How to Start a Compost Bin
Setting up a compost bin is simpler than you think. You can purchase a compost bin from a gardening store or make your own.
Start by layering organic waste with dry materials, like leaves or newspapers, to balance "green" and "brown" materials. Keep the pile moist and turn it regularly to help with decomposition.
What to Compost
Not all food waste is suitable for composting. Items like fruit peels, vegetable scraps, and eggshells are perfect for composting.
However, you should avoid adding meat, dairy, and oily foods, as they can attract pests and slow down the composting process.
Educational and Awareness Strategies
Food waste management is more than a personal responsibility—it’s a collective effort.
Educating yourself and your family about food waste can help foster lifelong habits that minimize waste.
Tracking Household Food Waste
Start by tracking how much food your household wastes each week. This can be done with a simple journal or a dedicated app like Food Rescue.
Seeing the numbers can help you identify patterns and areas to improve.
Raising Family Awareness
Involve your entire family in the effort. Teach children the importance of reducing waste by having them help with meal planning, grocery shopping, and food preparation.
Involving them in the process instills a sense of responsibility and awareness from a young age.
Zero Waste Challenge
Challenge yourself and your family to a zero-waste week. The goal is to throw away as little food as possible by using up leftovers, composting, and buying only what’s necessary.
This can be a fun and engaging way to see how much waste you can eliminate.
Community Initiatives for Food Waste Management
Beyond your home, there are numerous ways to contribute to food waste management in your community. By getting involved, you can make an even bigger impact.
Donate Surplus Food
If you have non-perishable items that you won’t be able to use, consider donating them to local food banks.
Many organizations, such as Feeding America, accept donations of surplus food to help combat hunger and reduce waste.
Food Waste in Local Communities
Look for local initiatives or businesses in your community that are committed to reducing food waste.
Farmers' markets, grocery stores, and restaurants increasingly participate in food waste management programs. Get involved and spread the word.
Conclusion
Reducing food waste at home is a powerful way to save money, protect the environment, and contribute to global food sustainability.
You can significantly reduce the amount of food your household throws away through careful planning, proper storage, composting, and smart use of technology.
However, managing food waste is only the beginning. To take your efforts to the next level, consider how food waste recycling can further minimize waste and create valuable resources.
At BurCell Technologies, we specialize in innovative food waste recycling solutions that turn waste into energy and valuable byproducts.
Contact BurCell Technologies today to see how we can help you succeed with food waste recycling and make a lasting impact on the environment.
FAQs
What is food waste and why is it a problem?
Food waste refers to any edible food that is discarded or lost before, during, or after preparation. It's a significant issue due to its environmental impact, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion.
How can I reduce food waste when grocery shopping?
Create a meal plan before shopping to buy only what you need. Check your pantry and fridge to avoid buying duplicates. Choose fruits and vegetables at their peak ripeness for longer shelf life.
What are some storage tips to prevent food waste?
Store fruits and vegetables in the appropriate conditions (e.g., fridge, pantry) to maintain freshness. Use airtight containers for leftovers to prevent spoilage. Label food with dates to track freshness.
How can I use leftovers creatively?
Plan for leftovers when cooking. Repurpose leftovers into new meals like soups, stews, or sandwiches. Freeze leftovers for later use.
What should I do with food scraps that can't be eaten?
Compost food scraps like vegetable peels, coffee grounds, and eggshells to create nutrient-rich soil for plants. Some communities also have food waste collection programs for composting or anaerobic digestion.
Why Food Waste Recycling Is Essential for Sustainable Living
In today’s world, food waste recycling is not just an option but an absolute necessity.
As the global population grows and resources dwindle, the need to find sustainable solutions for waste management has never been more critical.
Every year, billions of tons of food are thrown away, contributing to landfill overflows and greenhouse gas emissions that exacerbate climate change.
Food waste recycling offers a powerful solution to reduce this environmental burden and create a more sustainable future.
But what exactly is food waste recycling, and why is it essential to sustainable living?
Let’s dive into the environmental impact, benefits, and innovations in this vital field, shedding light on its potential for our planet’s future.
What Is Food Waste Recycling?
Food waste recycling is the process of turning organic waste—such as food scraps, leftover meals, and expired produce—into usable products.
Instead of sending food waste to landfills, where it contributes to methane emissions, food waste recycling transforms it into valuable materials like compost, bioenergy, and even animal feed.
There are two primary methods of food waste recycling: composting and industrial recycling.
Composting is a natural process where organic waste decomposes into a nutrient-rich soil additive, often used to improve garden soil.
On a larger scale, industrial food waste recycling can involve processes like anaerobic digestion, where food waste is broken down by microorganisms in oxygen-free environments to produce biogas and nutrient-rich fertilizers.
Interestingly, food waste recycling fits perfectly into the circular economy model, where waste products are repurposed instead of discarded.
This closed-loop system reduces the need for new resources and minimizes the overall environmental footprint of waste.
Benefits of Food Waste Recycling for Sustainable Living
1. Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the most compelling reasons to embrace food waste recycling is its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
As mentioned earlier, when food waste decomposes in landfills, it produces methane.
By diverting food waste from landfills to composting or anaerobic digestion facilities can significantly reduce methane emissions.
A lesser-known fact is that anaerobic digestion not only prevents methane from being released into the atmosphere but also captures it to create biogas, a renewable energy source.
This biogas can generate electricity, heat, or even fuel vehicles, providing a clean energy solution that reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
2. Creation of Renewable Energy
Anaerobic digestion plays a vital role in producing renewable energy from food waste.
As organic waste is broken down, it produces biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be harnessed for energy production.
According to the American Biogas Council, the U.S. has the potential to power over 7.5 million homes annually using biogas produced from food waste.
In addition to biogas, the anaerobic digestion process leaves behind a nutrient-rich material known as digestate, which can be used as an organic fertilizer.
This dual benefit—energy production and soil enhancement—makes anaerobic digestion a cornerstone of sustainable food waste recycling efforts.
3. Soil Enrichment and Organic Fertilizers
Composting is another crucial method of food waste recycling that benefits both the environment and agriculture.
When food waste is composted, it breaks down into humus, a nutrient-rich substance that improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and promotes plant growth.
Composting not only reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, which can contaminate water sources but also plays a vital role in restoring soil health.
Healthy soils act as carbon sinks, meaning they can absorb and store atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Food waste recycling contributes to carbon sequestration and helps combat climate change by improving soil fertility and structure through composting.
4. Resource Conservation
The process of food waste recycling also helps conserve valuable resources.
Reducing food waste sent to landfills can minimize the resources used to produce, transport, and dispose of food. This, in turn, lowers the overall environmental impact of food production.
Moreover, recycling food waste helps reduce the need for virgin resources, such as water and energy, to produce new food
A Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) report suggests that reducing food waste by just 15% could feed more than 25 million Americans annually.
Recycling food waste and conserving resources can create a more equitable and sustainable food system.
The Role of Technology in Food Waste Recycling
Technology has revolutionized how we recycle food waste, making the process more efficient and scalable.
One of the most innovative technologies in the field is the BurCell System, which transforms food waste into energy and other valuable resources.
The BurCell® System enhances the digestibility of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (MSW), producing more biogas in a shorter time frame.
This technology also enables the recovery of mixed plastics and other materials for thermal conversion, making the entire process more efficient and cost-effective than traditional methods.
Other technological advancements, such as automated food waste sorting systems and smart composting bins, are making it easier for businesses and households to recycle food waste.
These innovations are critical in global scaling food waste recycling efforts and ensuring the process is as sustainable as possible.
How Households Can Contribute to Food Waste Recycling
While industrial food waste recycling is essential, individuals and households play a crucial role in reducing food waste at the source.
Here are some practical tips for reducing food waste at home:
- Meal Planning: Plan meals ahead of time and only buy what you need. This reduces the likelihood of food spoiling before it’s eaten.
- Proper Food Storage: Store food correctly to extend its shelf life. For example, keep fruits and vegetables in separate drawers to prevent spoilage caused by ethylene gas.
- Creative Use of Leftovers: Get creative by incorporating them into new meals. For example, turn last night’s roast chicken into a hearty soup or sandwich.
- Composting: Start a compost bin at home. Composting is a simple and effective way to recycle food scraps into nutrient-rich soil. Many cities also offer community composting programs for those who don’t have space for a compost bin.
By taking these small steps, households can significantly reduce the food waste they generate and contribute to a more sustainable food system.
Food Waste Recycling on a Larger Scale: Community and Corporate Initiatives
While individual actions are necessary, community and corporate initiatives can potentially drive large-scale change in food waste recycling.
Many local governments have implemented food waste recycling programs that allow residents to separate food waste from other trash.
Cities like San Francisco and Portland have pioneered these efforts, diverting significant amounts of organic waste from landfills and turning them into compost and energy.
Corporations, particularly in the hospitality and retail sectors, are also improving their food waste recycling efforts.
Many grocery stores are partnering with food banks to donate surplus food rather than throwing it away, while restaurants are adopting technologies that help them track and reduce food waste.
These large-scale initiatives reduce food waste and set a positive example for individuals and other businesses to follow.
The Future of Food Waste Recycling
The future of food waste recycling looks promising, thanks to continued innovations in technology and growing awareness of the environmental impact of food waste.
Governments worldwide are introducing legislation to encourage food waste recycling, and many cities are setting ambitious goals to achieve zero waste.
For example, the European Union has set a target to halve food waste by 2030 as part of its broader sustainability agenda.
Meanwhile, innovations in biogas production, composting, and waste-to-energy technologies continue to improve the efficiency and scalability of food waste recycling efforts.
As more individuals, businesses, and governments embrace food waste recycling, we can expect to see a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, improved soil health, and a more sustainable food system overall.
Conclusion
Food waste recycling is an essential component of sustainable living.
Recycling can help mitigate climate change, conserve valuable resources, and generate renewable energy by reducing the amount of food waste sent to landfills.
Whether through individual efforts, community programs, or corporate initiatives, everyone plays a vital role in making food waste recycling a cornerstone of sustainability.
As we face growing environmental challenges, adopting food waste recycling offers a practical, impactful solution for a greener future.
To take your food waste management efforts to the next level, contact BurCell Technologies and see how we can help you succeed with innovative, efficient solutions tailored to your needs.
FAQs
What is food waste recycling and how does it benefit the environment?
Food waste recycling involves processing food scraps into valuable resources like compost or biogas, reducing landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions. It also helps conserve resources like water and energy used in food production.
Why is food waste a significant environmental problem?
Landfills are major sources of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. When food waste decomposes in landfills, it releases methane, contributing to climate change. Additionally, food waste takes up valuable space in landfills that could be used for other materials.
How can food waste recycling be implemented in daily life?
Composting food scraps at home is a simple and effective way to reduce food waste. Many communities also have food waste collection programs that allow residents to recycle food scraps for composting or biogas production.
What are the benefits of food waste recycling for communities?
Food waste recycling can create jobs in the composting and biogas industries. It can also help reduce the cost of waste management for communities. Additionally, compost produced from food waste can be used to improve soil health and increase agricultural productivity.
What are the challenges and solutions for scaling up food waste recycling?
One challenge is the lack of infrastructure and awareness about food waste recycling in many communities. To address this, governments and organizations can invest in building composting and biogas facilities and educating the public about the importance of food waste recycling.
The Importance of Solid Waste Management in Urban Areas
Solid waste management is one of the most critical challenges faced by rapidly growing urban areas.
As city populations rise and industrial activities expand, waste generation increases exponentially.
Managing this waste efficiently is crucial for the environment and public health, the economy, and the overall quality of life in urban areas.
Today, more than half of the global population lives in cities, expected to rise to 68% by 2050, according to the United Nations.
Without proper waste management systems, cities risk being overburdened with waste, leading to severe consequences for their residents and the environment.
In this article, we'll explore the importance of solid waste management in urban areas, diving deep into the strategies, challenges, and future solutions for maintaining clean and sustainable urban environments.
Understanding Solid Waste Management
Solid waste management is collecting, transporting, treating, and disposing of solid waste materials.
This process involves multiple stakeholders, from households and businesses to municipalities and private waste management companies.
It also includes the recovery of resources through recycling and composting and the responsible disposal of non-recyclable waste.
One of the critical challenges in urban solid waste management is the sheer volume and diversity of waste generated.
Urban waste includes residential waste, commercial waste, industrial waste, and hazardous materials.
Each type of waste requires different treatment and disposal methods, making waste management a complex and often costly task.
The Environmental Impact of Poor Waste Management
Improper waste disposal has far-reaching environmental consequences, especially in densely populated urban areas.
Without proper systems, waste often ends up in illegal dumpsites or landfills that lack safeguards to prevent pollution.
This can lead to significant environmental damage in the following ways:
Air Pollution
Burning waste is a common yet harmful disposal method in many urban areas where formal waste management systems are inadequate.
Open waste burning releases toxic fumes and particulate matter into the air, contributing to urban air pollution.
These pollutants harm the environment and pose serious health risks to city dwellers.
Water Contamination
Landfills, especially those not well-managed, can leach harmful chemicals into groundwater and nearby water bodies.
The runoff from these sites often contains hazardous materials such as heavy metals and toxins that contaminate drinking water sources.
This contamination can have devastating effects on ecosystems and human health alike.
Soil Degradation
When waste is improperly disposed of, it can degrade urban soil quality.
For example, plastics and other non-biodegradable materials can infiltrate the soil, reducing its fertility and harming plant life.
Over time, this leads to the loss of city green spaces, further exacerbating urban heat islands and contributing to climate change.
Cities like Jakarta and Mumbai have faced significant flooding due to clogged drainage systems filled with improperly disposed waste, particularly plastics.
This highlights how poor waste management practices can exacerbate natural disasters in urban settings.
The Health Risks of Inadequate Solid Waste Management
The link between poor waste management and public health is undeniable.
Inadequately managed waste creates breeding grounds for pests, contributes to air and water pollution, and spreads disease, particularly in overcrowded urban areas.
Spread of Diseases
Uncollected waste often attracts rats, mosquitoes, and other disease-carrying pests.
Piles of garbage can become breeding grounds for these pests, which can transmit diseases like dengue, malaria, and leptospirosis.
In cities with weak sanitation infrastructure, the spread of these diseases becomes a serious public health concern.
Impact on Urban Populations
Residents living near open dumpsites or landfills are at higher risk of developing respiratory problems, skin infections, and gastrointestinal diseases.
The toxic emissions from burning waste and the stench of rotting garbage create an unhealthy living environment that can lead to chronic health conditions.
Psychological Effects
Beyond the physical health risks, living in areas with poor waste management can take a psychological toll on urban residents.
Studies have shown that people living in unhygienic environments are more likely to experience stress, anxiety, and depression.
The constant presence of waste diminishes the overall quality of life and creates a negative perception of the community.
Economic Implications of Solid Waste Mismanagement
The economic cost of poor solid waste management is significant and can manifest in various ways.
From cleanup costs to lost revenue opportunities, the financial impact of mismanaged waste is often a burden on urban governments and businesses.
Cost of Cleanup
Urban areas with inadequate waste management systems frequently incur high costs to clean up illegal dumping sites and address waste overflow.
These cleanup efforts are expensive and labor-intensive, diverting resources that could be used for other essential services.
Impact on Tourism
A city’s cleanliness plays a crucial role in its attractiveness as a tourist destination.
Urban areas with visible waste problems—garbage-strewn streets or overflowing dumpsters—are less likely to attract tourists.
This loss of tourism revenue can hurt local economies, particularly those that rely on tourism as a significant source of income.
Missed Economic Opportunities
When waste is not managed correctly, cities miss valuable economic opportunities. Recycling programs, for example, can generate revenue by selling recyclable materials.
Similarly, waste-to-energy programs can convert waste into electricity or heat, providing a sustainable energy source for urban areas.
By neglecting these opportunities, cities are losing potential revenue streams that could be reinvested in improving public services.
San Francisco, a global leader in waste management, diverts 80% of its waste from landfills, generating significant revenue from recycling and composting programs.
This proactive approach has turned waste management into a profitable venture for the city.
Effective Solid Waste Management Strategies
The key to successful solid waste management in urban areas lies in implementing a combination of strategies that address each city's unique challenges.
Here are some proven strategies that cities can adopt to improve their waste management systems:
Segregation at Source
One of the most effective ways to manage waste is by segregating it at the source.
This means encouraging households, businesses, and institutions to separate their waste into recyclables, organic waste, and non-recyclables.
By doing so, cities can significantly reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and increase the efficiency of recycling programs.
Recycling Programs
Recycling is a critical component of any solid waste management strategy.
Cities that invest in robust recycling programs reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills and recover valuable materials that can be reused in manufacturing.
These programs also contribute to reducing the demand for raw materials, conserving natural resources, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste-to-Energy Technologies
Waste-to-energy technologies offer a sustainable solution to the growing waste problem in urban areas.
By converting waste into energy through incineration or gasification, cities can reduce their reliance on landfills while generating electricity or heat for urban populations.
Composting
Composting is an eco-friendly way to manage organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings.
By turning organic waste into nutrient-rich compost, cities can reduce landfill waste while creating valuable products for urban agriculture and landscaping.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Raising awareness about the importance of proper waste management is crucial for the success of any waste management strategy.
Cities should invest in public education campaigns to encourage residents to adopt sustainable waste disposal practices.
These campaigns can focus on recycling, composting, and reducing single-use plastics.
In Pune, India, an innovative waste management initiative led by local women’s cooperatives has successfully educated residents about waste segregation and collection.
This community-led model has been instrumental in improving waste management practices in the city.
The Role of Urban Governments in Solid Waste Management
Urban governments are pivotal in ensuring that solid waste management systems are effective, sustainable, and inclusive.
Their responsibilities range from enforcing regulations to investing in waste management infrastructure.
Policy and Regulation
Governments must establish and enforce strict regulations for waste disposal, recycling, and hazardous waste management.
These regulations should include penalties for illegal dumping and incentives for businesses and residents who adopt sustainable waste management practices.
Investment in Infrastructure
Urban waste management requires significant investment in infrastructure, including waste collection trucks, recycling facilities, and landfills with proper environmental safeguards.
Cities that invest in modern waste management infrastructure are better equipped to handle the growing waste problem.
Partnership with Private Sectors
Public-private partnerships can be an effective way for cities to improve their waste management systems.
By collaborating with private waste management companies, cities can leverage their expertise and resources to implement innovative waste disposal and recycling solutions.
Technological Solutions
Smart technology is transforming the way cities manage waste.
From smart bins that signal when they’re full to data-driven waste collection routes, technology is helping cities optimize their waste management operations.
These innovations not only reduce costs but also improve service delivery for residents.
Community Involvement and Behavioral Change
Successful waste management requires the active participation of urban communities.
Residents play a crucial role in reducing waste and ensuring that it is correctly disposed of.
Here’s how community involvement and behavioral change can improve waste management:
Empowering Citizens
Cities should empower residents to take ownership of waste management by providing them with the tools and resources they need to adopt sustainable waste practices.
This can include providing bins for segregated waste collection, offering incentives for recycling, and creating platforms for community involvement in waste management initiatives.
Innovative Programs
Some cities have implemented innovative community-led waste management programs that have been highly successful.
These programs often involve residents in waste collection, segregation, and recycling efforts, fostering a sense of community ownership and responsibility.
Importance of Behavioral Change
Changing waste disposal behaviors is key to the success of any waste management program.
Cities should focus on educating residents about improper waste disposal's environmental and health impacts and encourage them to adopt more sustainable waste practices.
Conclusion
The importance of solid waste management in urban areas cannot be overstated.
Effective waste management protects the environment, enhances public health, and drives sustainable economic growth.
By implementing the right strategies and engaging all stakeholders—governments, businesses, and residents—cities can create cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable environments for future generations.
If you want to take your solid waste recycling efforts to the next level, Burwell Technologies is here to help.
Our innovative solutions are designed to transform waste into valuable resources, maximizing efficiency and sustainability.
Contact BurCell Technologies today to see how we can help you succeed in solid waste recycling. Together, we can build a cleaner, more sustainable future.
FAQs
Why is solid waste management important in urban areas?
Solid waste management is crucial in urban areas to protect public health, prevent environmental pollution, and improve the overall quality of life. It helps to reduce the spread of diseases, minimize air and water pollution, and create a cleaner and more sustainable urban environment.
What are the common challenges of solid waste management in urban areas?
Urban areas face several challenges in solid waste management, including rapid population growth, inadequate infrastructure, lack of public awareness, and financial constraints. These factors can lead to inefficient waste collection, disposal, and recycling practices.
How can solid waste management contribute to sustainable development?
Effective solid waste management can promote sustainable development by conserving natural resources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and creating green jobs. It can also contribute to a circular economy by recycling and composting waste materials.
What are some innovative solutions for solid waste management in urban areas?
Innovative solutions for solid waste management include waste-to-energy technologies, advanced recycling techniques, and community-based waste management programs. These approaches can help to reduce the environmental impact of waste and promote sustainable waste management practices.
How can individuals contribute to better solid waste management?
Individuals can contribute to better solid waste management by reducing, reusing, and recycling waste, composting food scraps, and participating in community clean-up efforts. They can also support policies and initiatives that promote sustainable waste management practices.











